A study of two powerful earthquakes off the Alaska Peninsula in 2020 and 2021 shows a connection. They may be a part of an 80 year cascade along the fault.
The research was published in the journal Science Advances today, and was co-authored by Ronni Grapenthin of the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute. Revathy M. Parameswaran is a researcher at the UAF.
The Aleutian-Alaska megathrust fault, where the Pacific plate is sliding beneath the North American plate, may have brought shallow portions of the fault closer to failure after two deep earthquakes.
They say that their research will help scientists understand stress transfer and earthquake triggering in the region.
The megathrust fault is stressed by one large earthquake. Grapenthin said that this patch increases the stress on the next patch in the fault.
The first of the two major earthquakes happened in July of 2020. It hit near the Shumagin Islands south of the Alaska Peninsula.
The Chignik event occurred one year later. The epicenter was south of the Alaska Peninsula and northeast of the Simeonof earthquake.
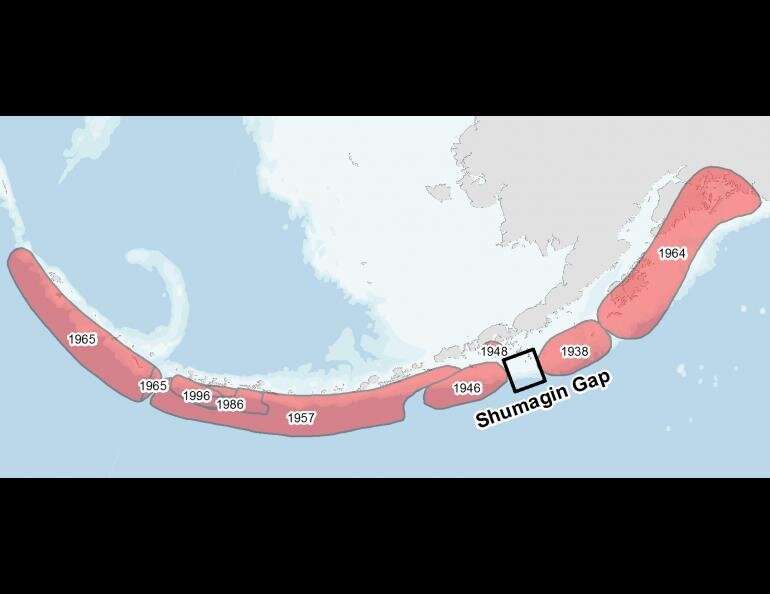
The Shumagin Gap is a place near the Shumagin Islands where two earthquakes and their aftershocks occurred. The tip of the Aleutian Islands is where the Pacific tectonic plate slides under the North American plate. Along the south side of the islands and the Alaska Peninsula, it goes up across the Kenai Peninsula and into Prince William Sound.
The Shumagin Gap, a space about 100 miles long in the subduction zone, had no major earthquakes until the 2020 and 2021.
This could be a case study to understand how adjacent earthquake patches could be activated by a significant release of energy that has accumulated through plate motion.
The data was studied to assess the impact of the stress changes caused by the 2020 Simeonof quake, which may relate to the Chignik quake.
The Chignik hypocenter is embedded in an area of increased stress change, consistent with what scientists know about how earthquakes are triggered.
Stress loading of the fault was indicated in the shallow regions of the model fault plane. According to the research paper, that area did not break during the earthquake.
The researchers said that the two earthquakes may be part of an 80 year cascade of large subduction earthquakes along this major plate boundary, with the most recent large event being the 8.7 earthquake off the Rat Islands in the 1960's.
Prior to 1965, there had been five earthquakes of magnitude 8 or greater from the farthest Aleutian Islands to south central Alaska.
The Aleutian-Alaska megathrust has released most of the stress that has accumulated since the beginning of that most recent cascade, according to Grapenthin.
More information: Julie L. Elliott et al, Cascading rupture of a megathrust, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm4131 Journal information: Science Advances Citation: Major 2020 Alaska quake triggered neighboring 2021 temblor (2022, May 4) retrieved 4 May 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-05-major-alaska-quake-triggered-neighboring.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.