March 13, 2020 by Zhang Nannan, Chinese Academy of Sciences
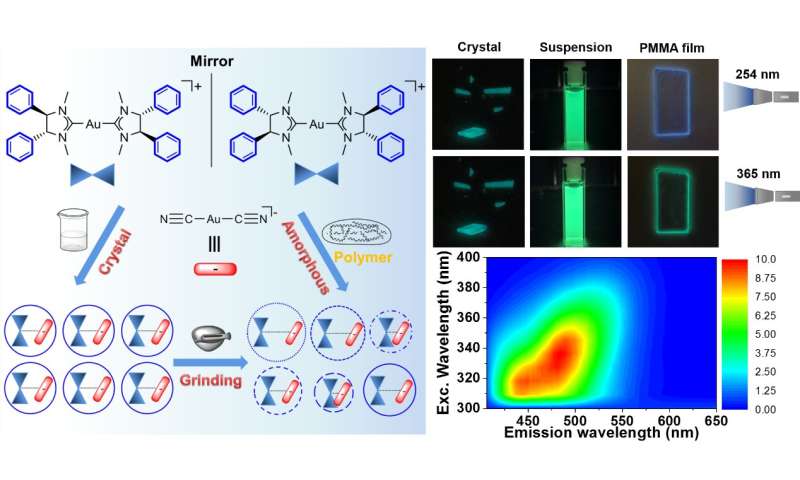
Smart materials especially for the dynamic physical stimuli responsive materials are being widely used. Wavelength-dependent (Ex-De) photoluminescent materials bring great interests to scientists, because their facile, non-invasive emission color tuning by switching the excitation wavelength.
Recently, research team led by Prof. Chen Yong from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (TIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported their new works on smart luminescent materials in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
In their work, they achieved excitation wavelength-tunable circularly polarized luminescence (Ex-De CPL) by controlling metallophilic interactions in chiral gold(I) double salts (RC-A and SC-A).
Different from the previous reported gold(I)-carbene double salt with infinite Au(I)···Au(I) chains, the new dimeric double salt shows discrete ion pairs with the cation and anion adopting an orthogonal configuration to each other.
The Ex-Ed CPL of RC-A and SC-A in poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) matrix are ascribed to originate from multiple emissive excited states as a result of the existence of varied Au(I)···Au(I) distances. The emission maxima can be dynamically tuned from 440 to 530 nm by changing the excitation wavelength from 300 to 400 nm.
The unique Ex-De CPL enable this material having promising applications in 3-D displays, quantum encryption, anti-counterfeiting and security-enhanced optical communications.
More information: Jian-Gong Yang et al. Controlling Metallophilic Interactions in Chiral Gold(I) Double Salts towards Excitation Wavelength-Tunable Circularly Polarized Luminescence, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2020). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202000792
Journal information:Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided byChinese Academy of Sciences