Multiple researchers at the Jackson Laboratory are participating in an ambitious research program that spans several top research institutions. Human health and the aging process can be helped byescent cells, which stop dividing in response to stressors. According to recent research with mice, clearing senescent cells delays the start of age related function and disease.
The health of humans as we age could be improved by removing senescent cells. The National Institutes of Health has launched an extensive research initiative to answer this question and more in order to advance human health.
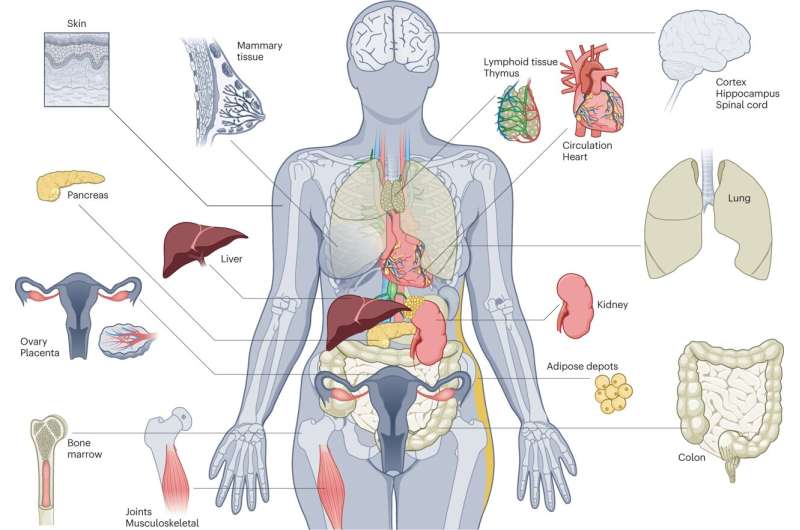
The SenNet Consortium was launched with centers to gather and analyze human data. The researchers will collect and analyze 18 tissues from healthy humans to understand the full scope of senescent cells and how they may contribute to the aging process.
A paper about the work of the SenNet Consortium was published.
JAX is going to make significant contributions to SenNet by profiling senescent cells in the heart, kidneys, and other tissues that are relevant to chronic diseases of aging. Diversity Outbred mouse populations, as well as inbred mice specifically engineered to help visualize senescent cell subsets, will be used by the team.
The JAX institutional initiative to continue to build the human-mouse interface is aligned with these efforts. SenNet wants to know more about senescent cell biology and build an atlas of senescent cells. The potential benefits of senotherapeutics for healthy human aging are exciting as are other possible clinical advances.
The SenNet Consortium is trying to map senescent cells throughout the lifespan. DOI is 10.1038/s4358
Journal information: Nature Aging
Citation: Consortium to map senescent cells and their effect on aging and human health (2022, December 29) retrieved 29 December 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-12-consortium-senescent-cells-effect-aging.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.